Security: Efficiency Objective. Loss Control Unknown.
Efficiency: It is the relationship taking compliments targets for the costs of the means used for this purpose. It is the ideal of private enterprise.
How to improve the bottom line of your business. If you really care about the EBITDA will read this article. How to reduce losses. Aimed at all responsible managers or concerned about getting the best results for your business, the business entity.
Break the myth that security spending item can not contribute more than that "expenditure". Safety is and should be an investment, as such, aportarnos should benefit both intangible and tangible.
In this article I will give you the keys to improve the outcome of Ebitda in your business. The purpose of EBITDA, know it's, obtain an accurate picture of what the company is winning or losing in the core business. Well, paragraph of losses is still much to scratch. Have clearly identified all losses? Know unprofitable processes? Do you know what percentage of shrinkage in business?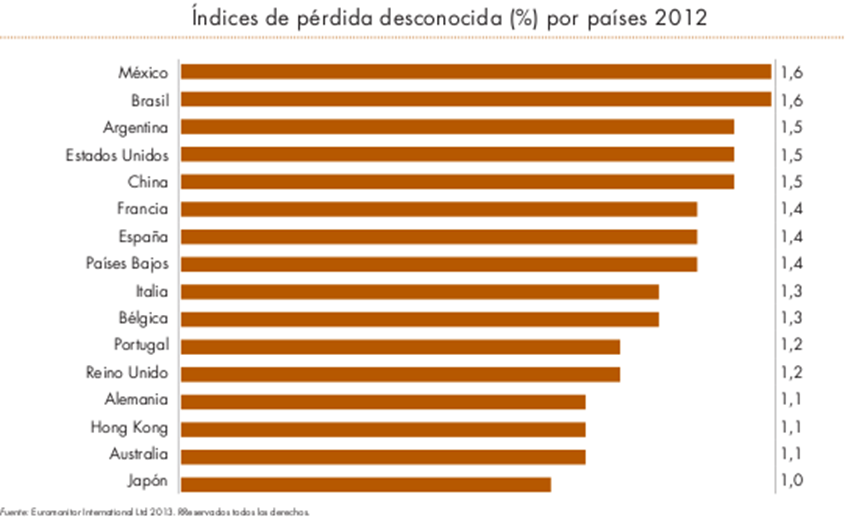
Before I go and for those who are not familiar with the concept, clarify that the Unknown loss is the difference of Stock, namely, the difference between the underlying stock and we should have the actual stock we have.
In its broadest sense, shrinkage is missing or not registered devaluation of other goods and resources of the company out of the loop of goods sold, as may be, work tools, office furniture, etc.. And finally, understanding the term in all its breadth, also other losses caused by the negligence or dishonesty of employees, suppliers and customers who have not come to be identified or recorded, phenomena beyond the theft or administrative errors. Ej.: Accidental loss, losses, perishable control, sabotage, etc.. In these cases, As with theft, are the effects but no one knows who or what has caused. These negative effects will be also in opportunity cost.
Difference from the known losses. Thefts detected, quantified theft, accidental losses, and in general, any loss manifests and registered, not counted as shrinkage, but as known losses. Only when there are identified and their effects are not properly recorded, fed back into the section shrinkage.
Spain has the dubious honor of being the head of theft and fraud in the distribution sector (small and large businesses) European retail. A recent study shows that in Spain the average shrinkage rate is in the 1,4%, of total sales, namely, 2.617 Million € uros (437.039.000.000 million pesetas). AWESOME TRUTH! Well, these billions are lost each year in stores in Spain. Worse, according to the World Barometer conducted in 2010 the rate of loss was in a 1,36%, we have increased 0,4% our index, is not a good thing nor a good trend.
Eye! I emphasize that the indicator 1,4 % is the industry average (the great variability of figures provided by employers indicates a reluctance to acknowledge the problem for some companies, and ignorance of the actual data in other), This means, that businesses that do not have adequate security measures implemented and process control, or measures having improperly managed, may be placed around the 2% shrinkage, this figure being the one that comes closest to the actual average. To clarify the importance of this data put 2 Examples of current reality:
1.- A small Super checking in 1.000.000 Total annual sales of €. Lose 20.000 € / year.
2.- A chain of hyper that you check 500.000.000 €, lost annually 10.000.000 €.
The multiplication is simply, calculates yourself with this example where they may be located your losses.
A desirable situation would place the loss rate in the 0,50% in 2 years old, and hold it there with adequate investment.
Where does the loss Unknown?
Shrinkage is composed: Internal Theft (35,9%), Shoplifting (32,2%), and Administrative Errors (31,9%). This consideration Losses unaccounted natural and accidental losses unregistered included under the heading of administrative errors being unaccounted losses.
The percentage of companies that have data and are able to answer about is very small (17,6%), so the results should be taken with some caution.
Internal Theft
It is the theft committed by employees of the company, as well as foreign employees occupationally related, which is also understood as internal theft, because suppliers and subcontractors often have the same access privileges to the employees of the company.
Statistically there are fewer thefts frauds via the internal to external route; but at elevated amounts routinely treated, significantly increases the overall number, equated with shoplifting losses.
International data. The annual report of the London House and the Food Marketing Institute on employee theft in supermarkets reflected that: The 90% of staff had been involved in dishonest behavior, the 32% recognized eating food without paying, the 29% said to have declared no spending tent material, the 22% had purposely worked slowly, the 17% was absent without legitimate excuse and 50% had simulated an injury or illness (Ej.: Excuse flu). The average theft for all employees currently reaches 5 € / employee / week, what year is € 260 per employee.
The U.S. Chamber of Commerce. estimated 30% of all business failures are related to some kind of internal theft. Fraud generally costs the U.S. economy between 2 and 5% GNP, so you can get to make it the crime of the century.
Shoplifting
It is mainly petty theft of goods by customers themselves or organized gangs, currently booming. Examples:
- Robo Ant: The hurtador gets into his pocket and continued the item hanging around the property, if they perceive that they have not found him hiding is carried, if they find, before reaching box will quit and will claim that he had no car or bag and he forgot it in his pocket. Petty thefts that dropwise become big losses.
- The Change. People changing tags to alter the actual cost of the products by a lower one.
- Las falderas. It coats the falda prepared with hidden funds. In groups of up to five people, hiding the loot in their clothing or foil packets to circumvent panels Burglar Store.
- Robo diaper. Women with children in arms: Hide merchandise between diapers and are less able to puncture the baby with a needle or pin to do mourn; thereby distract the Vigilante and get away with the fact.
- In Group. Bands 10 people are divided into groups, in order to place screens and electronic products in cart super, Property for run, while others distract security personnel and one or two more await the merchandise in a moving vehicle, where fleeing.
- Gum: This type of theft occurs mainly in jewelry. The offender paste gum under the counter and when I show the parts, steal one and the gum hits. If the worker is aware, the offender denies having done and can not proceed against. If the worker does not realize, subsequently collects an accomplice piece stuck to gum.
- Capote: one of the criminals makes leaving the worker behind the counter and a large bag or obstructs vision like desk worker, another time the offender fail to access the back of the counter and steal money or items.
- Handkerchief: the offender pretends to be cold and a bad cough. With the help of a tissue steals objects.
- Bag with an inner lining of aluminum foil: these bags homemade preventing malfunction of the security chip mounted in the articles, to go through the metal detector door listing.
- Distraction worker or Vigilante: offenders act in groups and, while some distract and deceive the seller or Vigilante, consume other theft.
- Spot: this type of theft does not directly affect the establishment but to customers and, often, the wrongful act begins in the shop. En este caso los delincuentes también actúan en grupo, y consiste en que uno de ellos tira un líquido (café, chocolate, etc.) sobre la ropa de la víctima y enseguida le ofrece ayuda para limpiarle, mostrándose muy preocupado y dando excusas de forma reiterada. Este descuido es aprovechado por un segundo delincuente para consumar el hurto.
Otras vías de pérdida
Errores administrativos: Son aquellas pérdidas causadas por errores de apreciación cuantitativa o cualitativa no intencionales, siempre que pasen desapercibidos.
Mermas naturales: Son aquellas pérdidas causadas por efectos naturales y que no han sido tomadas en consideración.
Accidental loss: Al igual que ocurre con los errores administrativos, las pérdidas accidentales las forman por definición accidentes no intencionados cuyas causas o efectos no han quedado registrados.
Deficiente gestión logística. Gestión de perecederos, ubicación de productos, etiquetados incorrectos, alarmados deficientes, etc..
La pérdida desconocida tiene una repercusión directa sobre la cuenta de resultados, y no es inusual que pueda llegar a superar los beneficios netos. The 1,4% de pérdida desconocida indicado resulta una cifra preocupante si tenemos en cuenta que los márgenes de beneficio de las empresas de distribución se han reducido considerablemente y se sitúan entre el 2 and 3%. Esto significa que se está perdiendo buena parte de ese margen por falta de control efectivo de los productos, lo que hace que cualquier mejora se traduzca inmediatamente en incremento del beneficio neto, convirtiéndose así en una nueva vía de ingresos. Controlling shrinkage supposed, therefore, a basic necessity for businesses who want to increase their profits.
Perfect, Brilliant! I will say, and the first question is how much, how and, to begin what should I invest in security to achieve desirable place myself in that index 0,5%?
According to a study AECOC, companies invest in safety 0% the maximum it 0,8% of total sales. Obviously a wide range and the maximum investment not always guarantees the best results. The goal is reached when the problem management specialists perform shrink, results focused and knowledgeable about the different, techniques, tools and procedures for each case.
The How. The key to success is making "tailor-made" for each project, namely, 1º analyze, 2º evaluate and plan, 3º implement the tools and resources to adequately manage 4th. This key success should be expressed in a DIRECTOR LOSS PREVENTION PLAN INTEGRAL integrated PLAN ON SELF entity, the installation business.
The The. The experience and success stories well managed, show that to get through the 2% to the 0,5% should be seen as in any business plan to an investment 3 years old. First year, investment on turnover 0,5%. Second year 0,4% and third year 0,3%. These well-managed by the implementation of investments mentioned PLAN, not only guarantee full repayment of security expenditure, also provide an economic benefit that is reflected in the income statement by reducing shrinkage and known.
We will see more clearly using the example 2 Loss in Hypermarkets.
BILLING 500.000.000 € with 2% Loss in 3 years lost 30.000.000 €
INVESTMENT IN SAFETY 1st. Year 0,5% € 2.5 million ..........
INVERSION EN SEGURIDAD 2º Año 0,4%………2.000.000 €
INVESTING IN SECURITY 3rd. 0.3% Year………1.500.000 €
TOTAL = 6.000.000 €
- Continuing with our example when the target is located in the 0,5% loss would 2.500.000 € annual, in three years 7.500.000 €.
- Against 30.000.000 € the one difference in favor of 22.500.000 €.
- Subtracting investment in security to three years of 6.000.000 € obtain the FINAL RESULT OF 16.500.000 € net profit in three years to the income statement.
In what, I must invest to develop the project to reduce loss.
"As a security professional and expert in shrink I offer you the opportunity to contact me through the contact form on my Blog. Working in a company that integrates security solutions for all loss control and I can design, implement and manage time, a project tailored to your business ".
The investment to be made involves a number of components, necessary as all links in the same chain, each with a specific function and mission. I emphasize the most important, the difference between success and failure of our loss reduction target will be the management and coordination of components, these are:
No component 1. Service of a specialist professional security consultant with experience and knowledge in the area of shrinkage. This consultant should provide advice and practical help. Simultaneously, should help to managers in improving management practices and safety protocols and processes that impact the loss, and performance and monitoring individual and collective functions.”
Model type of the different phases of the work of Consultancy:
Initiation (initial preparation):
- First contact with the customer
- Preliminary Diagnosis
- Plan the task
- Motion Task
- Contract
Diagnosis
- Get on to
- Analysis and synthesis
- Detailed consideration of the problem.
Planning measures (Action Plan)
- Develop solutions
- Assess options
- Customer Proposal
- Plan the implementation of measures
Application (implement)
- Contribute to the implementation
- Motion Match
- Training
Termination
- Evaluation
- Final Report
- Set New Goals and Commitments
- Monitoring plans
No component 2. Security Guard, knows the idiosyncrasies of this sector, with specific training. The functions and protocol to follow should be detailed in the Master Plan. Highlight a strong possibility of contracting in filling the critical or needed times, for coverage is fair and necessary to target customer.
No component 3. Electronic Security Systems, essential component in any type of establishment and of vital importance to the topic at hand. Pero atención al esquema y a los equipos que se instalen. Es en este componente donde puede haber mayores variaciones en los precios, y lo que es más importante, en muchas ocasiones he comprobado personalmente que después de haber realizado una importante inversión los equipos (hardware y software) no cubren las necesidades y objetivos a cubrir.
La elección del tipo de cámara para cada punto del CCTV, los diferentes tipos de grabadores y en especial el sistema para control de línea de caja y TPV debe ser minuciosamente estudiado. Personalmente he trabajado con un software de gestión para línea de cajas que no tiene competencia a nivel mundial, por todas las prestaciones que aporta y por el precio de su implantación, la mitad de lo que cuesta el que más se le acerca pero sin llegar a identificar elementos clave que impactan en la pérdida.
On the other hand, I mention these teams they can add value and net income, if its added capabilities are optimized for marketing, Business and HR.
No component 4. Connection to CRA (Central Alarm Receiving), not simply be connected and warn you when the alarm goes. A good connection management protocol should be established, disconnects and track individual items to monitor and report, a video-surveillance well structured will give us valuable information.
No component 5. Service Viewing Images, linked to electronic systems and management and imaging, we must provide the software discussed in component # 3. The viewing through these teams, allows intelligent searches for pre-programmed searches incident or request, resulting in a savings of time and therefore many more viewings points relative to other systems. People envision should have experience in the detection of fraud or bad business practices and can be included in this service similar reports to those of the mystery shopper or mystery shopper (en inglés mystery shopper) is a technique used by companies to assess and measure the quality of customer service.
No component 6. Special Security Service Inspectors, previous delegation of functions by the Security Jeje Security Company contracted for the surveillance and will cover the vigilantes in the case of plants with high rate of shoplifting.
No component 7. Training. Divide into two sections, 1.- security personnel that integrates the Security Master Plan. 2.- client personnel that integrates (managers, area managers and line workers, This training focuses on problem awareness and self, se realiza mediante charlas programadas y tiene como objetivo la implicación y motivación de todas los empleados en la reducción de la pérdida.
Un efecto demostrado de estas charlas de formación es la disuasión de determinadas prácticas laborales no deseadas y la disminución del hurto interno, demostrado estadísticamente. En estas charlas, se aprenden medidas básicas de seguridad y autoprotección, modus operandi de los hurtadores, psicología enfocada a la seguridad, medidas contra el fraude, etc.. El programa de formación se consensua con el cliente y se detalla en el Plan Director de Seguridad.
No component 8. Servicio de gestión de denuncias. Para determinados volúmenes de denuncias, resulta muy rentable la contratación de este componente absolutamente profesionalizado y automatizado, con experiencia y con cobertura nacional. Este componente se detallará en el Plan Director de Prevención de Pérdida.
Para la aplicación de estos 8 componentes existen muchas combinaciones, muchas decisiones posibles, y solo una es la mejor. Cada tipo de establecimiento tiene sus particularidades, con sus propias y únicas áreas de riesgo, con una causa y una solución adaptada diferente.
Todo buen sistema de seguridad debe ser integral, ha de contemplar todas las posibles vías de pérdida, no debe dejar huecos de supervisión. Además ha de ser un sistema integrado, debe ser compatible con los demás objetivos de la empresa. Ej.: Objetivos de marketing, de merchandising, de imagen, etc.. No olvidemos que el objetivo principal es conseguir aumentar los beneficios.
X Reasons to be controlled Unknown Loss.
The increased competition is causing a gradual reduction of trade margins. The reduction in net income brings an increase in the relative importance of the phenomenon. This reduction in net operating income leads to a reduction of costs needed to maintain competitiveness.
The information age. The information is going to be the nucleus from which the added value of good corporate governance creates. Information is a useful and valuable in the service of a goal: Achieving competitive advantage. Ej.: Through making the most efficient and accurate decisions. Information to prevent losses. Information for sell better without increasing exposure to fraud.
Culture and consumption satisfaction is shifting moral values. Aggressive advertising creates dissatisfied individuals who want "as" possessing certain goods (I do not mean the parent who steals a loaf of bread, a kilo of arroz or a liter of leche), I mean perfumery, clothes, alcohol, electronics, smoked or deli products called.
The distribution is characterized by accumulations of money and merchandise, as well as constant replacement flow. Such movement of values makes it the perfect breeding ground for theft, over time represents an opportunity and temptation to ignore difficult if proper measures are not taken.
La pérdida desconocida esconde un problema de eficiencia que no sólo afecta a los distribuidores finales, sino que se transmite a lo largo de toda la cadena de suministro, con importantes repercusiones para fabricantes y consumidores, ya que en ocasiones se repercute sobre el precio de determinados productos un margen destinado a paliar su alto índice de hurto.
El coste defensivo puede considerarlo como un mal menor y como una inversión razonable, tal y como te he demostrado con los ejemplos de cifras anteriores, si cumple sus objetivos con eficiencia.
Minimizar los costes legales. Son los costes derivados del comienzo y desarrollo de un proceso legal. Ej.: Abogados, asesoría, tiempo dedicado a las gestiones, denuncias, etc..
Coste por desajuste de inventario. El inventario no es más que un coste más derivado del desajuste provocado por la pérdida desconocida, un desajuste que hace necesaria una comprobación física porque el inventario permanente queda desajustado. Si no hubiera pérdida desconocida no sería necesario realizarlo porque correspondería al teórico. Ej.: Al registrar la devolución fraudulenta se actualizarán erróneamente las cifras del inventario.
Destrucción del producto en el acto del hurto. Cuando el hurto pasa, quedan los restos. En el mejor de los casos te encontrarás con alimentos medio comidos o sólo con las envolturas.
Coste de reemplazo. Es el gasto provocado por la manipulación adicional de productos que supone el proceso de reposición. Ej.: Gasto del transporte de productos adicionales. El bien o artículo hurtado debe ser reemplazado, lo que posiblemente deba realizarse en condiciones de compra diferentes a aquellas en las que se adquirió.
Reposición por la vía comercial. La reposición por la vía comercial significa pagar el importe del bien o artículo hurtado con el beneficio neto obtenido por la venta de productos adicionales. Esta es la forma natural de reposición de la pérdida desconocida. Descubrir lo costosa que puede ser le servirá de acercamiento al esfuerzo real que supone la pérdida desconocida:
Example 1. El “inocente almuerzo”: Un empleado cada día a la hora del almuerzo coge una lata de conservas, bebida, o cualquier otro producto por valor de 1€, realiza esta actividad durante todo el año. Contando 204 días de trabajo, este pequeño hurto mantenido continuadamente se convierte en 204 €uros de pérdida. Si el beneficio neto del establecimiento es del 2%, deberá vender 10.200 €uros en productos ¡Sólo para compensar la pérdida! Expresado en latas, supondría tener que vender ¡10.000 latas más! Y lo peor de todo es que este trabajo en vano se realiza en favor del beneficio del hurtador, frecuentemente protegido por la complicidad y aprobación de los compañeros que no conocen las implicaciones del problema.
Example 2. Shoplifting: Si cada día una persona hurtase un artículo por valor de 10€, el establecimiento dejaría de ingresar 2.000€ al año, si suponemos que está abierto durante 200 días, teniendo en cuenta el margen del producto, a 2,5% for example, la cantidad de producto adicional a vender para recuperar los ingresos perdidos sería: 2.000 / 2,5 = 80.000 €uros, namely, 8.000 unidades más del producto en cuestión.
Coste público. La Administración Pública deja de ingresar los impuestos correspondientes a la facturación empresarial desaparecida, el capital o mercancías desviados rara vez pagarán impuestos, al ser beneficios ocultos. La economía del país, en su conjunto, pierde competitividad al aumentar los costes de la empresa.
Carga a los clientes. Directa: Cuando el cliente sufre directamente las consecuencias de un hurto o abuso. Ej. 1: Cajero que entrega al cliente menos cambio del correspondiente. Ej. 2: Cuando el cliente observa, al llegar a casa, que faltan piezas del producto en blíster que ha comprado, con la consiguiente pérdida de tiempo en su devolución. Indirecta: Cuando la pérdida desconocida desencadena un incremento del precio.
Coste de competitividad. El incremento de costes derivados del hurto llega a reducir los recursos de la empresa así como su competitividad respecto al precio. Una competencia que haya solucionado aceptablemente el problema puede causar estragos comerciales mientras usted se dedica a cubrir costes. En muchos casos, la pérdida desconocida puede suponer la diferencia entre el éxito o el fracaso de un negocio.
Costes de marketing. Coste de surtido. El alto riesgo de hurto de algunos artículos de elevado valor hace muy difícil su exposición abierta o desprotegida en establecimientos de autoservicio, lo que imposibilita su comercialización masiva.
Costes de merchandising. Se crean barreras que obstaculizan el contacto directo del cliente con el producto. Ej.: Vitrinas, mostrador. La falta de contacto directo con el producto frena las compras impulsivas. Also, encerrar los productos obliga a ocupar tiempo del personal en hacerlos accesibles.
Costes de Imagen. Hacia los inversores: An uncontrolled shrinkage, dishonest or incidents that have taken stir and Advertising, can seriously affect the credibility of the company to investors face, losing prestige as a solid value, although intuitions concerned to real problems. Some investors may get to play the good or poor control of shrinkage as an indication of good or bad management of those responsible.
Problems with employees and unions: Companies employing corrective preventive measures before they deteriorate can see how their relationships with employees and union. Ej.: When situations of dismissal motivated by internal theft occur, or when they feel controlled excess, employees may lose motivation, thus fostering the spirit of rebellion. Conversely, if they are trained in preventive objective of Component No. 7 explained above, cases of dismissal for theft are reduced and employees and unions accept it as a move that frees them from the "bad apples".
Opportunity cost. The opportunity cost is the cost resulting from the potential gains that could generate the target capital if they had invested in a different activity to the replacement of losses.
CONCLUSION
The importance of the costs generated by the shrinkage in the income statement of a business is essential to making urgent preventive and corrective measures. The implementation of these measures through the above components should be implemented after a study and report of personal performance.
If you want a comprehensive solution to the problem please contact me, email me from the contact form on the right of the Blog.
If you liked this article, leave me a comment and share it all, can we help someone.

Muy buen artículo.
Gracias Enrique. Regards
Le agradezco por su aporte, definitivamente el tema de seguridad y control de pérdidas es integral y afecta directamente al ciclo productivo en todas sus etapas de gestión. El costo logístico de la oportunidad para beneficio de la gestión es un tema básico a sumar y dentro de ello las labores que el transporte puede generar, como bien se menciona un análisis de los riesgos eficiente pueden prevenir estas pérdidas desconocidas. Regards
Gracias a ti Jaime por tus comentarios.
Regards,
Ferran
Ferran….
Excelente documento, muy didactico…Quizas lo unico que adicionaria seria los hurtos internos ocurridos en el despacho de productos a transporte interno/externo, confabulacion entre colaborador del almacen y transporte (mercaderia entregada de mas, vehiculos con doble fondo, etc.).
En todo caso una valiosa contribucion en como abordar el tema de las diferencias de inventario, dada la importancia que ello tiene en los costos logisticos..Por supuesto el domuento merece ser compartirlo entre profesionales asociados al tema… Mis felicitaciones por compartir conocimiento..
Regards
Hola Germán,
Thanks for your comments.
Un saludo cordial,
Ferran
gracias pro el artículo, muy instructivo.
gracias por tus palabras Samira, un saludo.
excelente redaccion claro en todo aspecto , estoy buesnado un trabajo con respecto a esta area favor orientame en mas ideas
MUY INTERESANTE ….ME GUSTARIA REALIZAR UN CURSO CON USTED…
Buenas tardes, hola Sr. Ferran, actualmente soy gerente de seguridad de un importante mercado de la mas grande cadena de mercados en venezuela, nuestro actual problema se debe al hurto interno, y es que el sistema legal de justicia no aplica a muchos tipos de hurto que se cometen en venezuela, si una persona es capturada robando carne la fiscalía lo lo procesa porque según es comida, y con los empleados ya tenemos un sin fin de procedimientos con personal robando, nosotros realizamos el procedimiento, pero a la semana esta nuevamente el empleado trabando en el mismo puesto de trabajo y continua robando cuajado de la risa.
Estimado Jose,
Según me comenta usted el problema principal es el hurto interno y la falta de leyes que penalicen el mismo.
Venezuelan law do not know but I understand that both legally and business should be measures to avert and penalize disloyal employees,es…si lo que se requiere son pruebas fehacientes que demuestren los actos ilícitos, existen medidas y sistemas de seguridad que pueden aportar las pruebas necesarias y periciales para que legalmente pueda despedir al trabajador que defrauda. Si no se adoptan las medidas ejemplarizantes, a largo plazo se hundirá el negocio y todos los trabajadores perderan junto con los propietarios del mismo. Suerte y ánimo.
Un saludo desde España.
Ferran R.
Good Morning! I loved your article,,es,really interesting,,es,I work in a security company and I would like to ask you a question,,es,Why should an entrepreneur invest in controlling the unknown loss,,es,It is clear that it is a great benefit for him,,es,but how could it be transmitted,,es,Thank you,,es,Thanks for your words Fco,,es,Jose,,en,It is always necessary to invest in controlling the loss,,es,yes,,es,proportional to the magnitude of the problem to obtain profitability,,es,Each case needs a customized solution,,es,from my experience everything is susceptible to improvement and from my point of view,,es,the control and prevention of the unknown loss is a way to always improve the income statement of a business,,es, realmente interesante.
Trabajo en una empresa de seguridad y me gustaría hacerte una pregunta.
¿Por qué debería invertir un empresario en controlar la pérdida desconocida?
Está claro que es un gran beneficio para él, pero como se lo podría transmitir
Mil gracias
Gracias por tus palabras Fco. Jose.
Siempre es necesario invertir en controlar la perdida, eso si, de manera proporcional a la magnitud del problema para obtener rentabilidad. Cada caso necesita una solución a medida, but, por mi experiencia todo es susceptible de mejorar y bajo mi punto de vista, el control y prevención de la perdida desconocida es una manera de mejorar siempre la cuenta de resultados de un negocio.
Ferran