Is enormous potential that is already providing this security technology, data systems and different processes, both in business and in the management of any public or private entity. In this article I will explain, What is the RFID, how it works, which applications have, how it benefits and examples of success stories already in place.
Such is the projection of efficiency and effectiveness provided by the RFID, in the coming years many projects management, quality, control, logistics and security, will integrate this solution as up any computer system.
The information I share in this article, It is drawn primarily from the work of; Area Studies of the National Observatory for Telecommunications and the Information Society (ONTSI), AETIC, Association of Electronics, Information Technology and Telecommunications of Spain and with the Technical Assistance AT4 wireless.
As we will see throughout the document makes RFID system competitive managing any company or entity where applicable. Medinate all the location, traceability and identification of objects and people (respecting their privacy). Of note is the high potential social and economic benefits provided by the RFID.
WHAT IS IT AND HOW THE RFID?
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) is capture technology and automatic identification of information in electronic tags (tags). When these tags come into the coverage area of a RFID reader, it sends a signal to the tag to transmit the information stored in its memory, without the need for physical contact there is the visual (line of sight) between the reader and the tags, unlike bar code reading needs of direct view and very close.
Among the most influential factors in the spread of the use of RFID include aspects related to security and privacy, the initial costs of deployment, current price of RFID tags and inertia to undertake and manage change processes in many companies. Currently, all these aspects have improved, meaning that increasing solutions and services offered by the RFID will become apparent in many areas, the number of companies and organizations undertaking projects with this technology is growing every year.
Today we find systems that use RFID technology in a variety of services civil and military, public and private, such as identifying patients in hospitals, automatic payment on motorways, animal identification, etc..
The main feature that gives this identification system a great value, is that the RFID chip inside to store identifying information that gives each element labeled a single character.
In an RFID system, identifying the element (It may be an object, animal or person) is labeled with a small silicon chip attached to an antenna radiofrequency (known as' tag’ or label) so you can communicate and be identified, through radio waves, device for a transmitter / receiver (Known as 'reader') designed for that purpose.
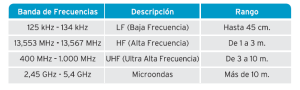
Frequency bands used in RFID. Source: (And ONTSI AETIC)
Depending on the functional requirements of the final application, automatic identification may or may not require, a greater or lesser distance identification, generate the least possible radio interference, signal stability against harsh environments or high ability to penetrate materials. According to the requirements are, and the frequency of the system is selected.
The basic components of an RFID system are: day, reader, RF antenna and information system manager.
a) RFID tag or label, in the field of electronic "transponder", It is the flagship component of the RFID system. It is called "transponder" device by its basic mode of operation, has the capacity to receive and transmit signals, but only transmitted as a response to a possible request for a "transceiver" device or RFID reader. The tag is a small chip, or circuit integrado, an antenna adapted to radiofrequency
(RF) allowing radio communication. These elements integrated on a substrate, form what is known as tag.
Depending on the final application of the identification system, the substrate and the chip is encapsulated RF antenna will be different allowing the adaptation of its features to application requirements, for example there are special tags for textile, Flows, metals, books, etc..
The tags have very different features or capabilities, so we can make multiple classifications to help us understand how they affect your behavior or way of working.
We could classify tags by type (active, passive and semi-active), memory by type, storage, Power source, working frequencies, Physical characteristics, air interface protocol (how it communicates with the computer reader) and so on with almost every feature.
The choice of the label or "tag" is a proper key for the success of RFID application factor and its contribution to the production process.
There are many basic features that can modify the behavior of an RFID tag, some common to all tags (minimum requirements that must meet all) and others that are just as model.
• Adhesion tag: any type of tag must have an adhesive or mechanical mechanism to attach the object.
• Reading Tag: Any tag must be able to communicate the information by radio frequency.
• Kill/Disable (disqualification): Some tags allow the reader to send a command (order) to stop working permanently, provided they get the right "Kill code". This causes not respond anymore.
• Write Once (Write Once): Many tags are introduced in the manufacture identification own, but containing writeonce feature allows the user to configure or write its value only once; after modifying the initial, is impossible to change.
• Write many (various scriptures): Some tags have the ability to write and rewrite as many times as desired (There is usually a very high limit cycles, eg 100.000 scriptures) the data field identifier.
• Collision: When many tags next to a reader, it can be difficult to "speak" or communicate with them at a time. The anti-collision feature allows the tag to know when to transmit not to hinder or annoy other readings. This feature is performed using protocols that control communications between tag and reader.
• Security and Encryption: Some tags encrypt the communication information, there is a possibility in several types of these tags to respond to readers who only gives them a secret password.
• Supported Standards (accordance): Tags may comply with one or more standards, allowing communication with readers which comply.
Another feature is the power mode. Passive tags obtain power transmission reader, assets using its own battery and semi active or semi passive use a battery to activate the chip circuitry to generate energy but communication is collecting radio waves reader (and liabilities).
b) The reader device, in the field of electronics "transceiver", acts as a transmitting station identification request signals to the tags and getting the answers to these requests. It is a receiver / transmitter device within, incorporates besides the transmission and reception subsystems, digital signal processor that gives it more functionality and complexity in their operations.
A reader, need one or more RF antenna for transmitting the generated signal and the response from the tag. Readers may find the RF antenna built into its own hardware and readers with external antenna RF connectors. Depending on the final application field, will need to have a configuration or other.
For the identification of animals or even hospital patients, as usual is to have handheld reading devices, PDA type, in which the antenna shown integrated in the reader itself. In the case of a distribution center or warehouse, in which identification is located in a passageway or check, reader devices are used with various external antennas that enable an arc configuration identification delimiting a specific area of reading.
c) Database Additional software is a platform that allows you to store, organized manner, identification information generated by the hardware subsystem (tag and reader).
Without this subsystem software, a client would be unable to manage the information generated by a reader. Prior to this step, you need to store identification information in a common format so that any client application, higher level of, be able to work and access this information. Between the database and the device reader interface middleware running Pretreat raw data generated by the reader is necessary.
Main features and application examples of different frequency bands used in RFID.
Main benefits of RFID technology.
Many industrial sectors can benefit from the advantages of RFID technology (RFID). These benefits derive primarily from the optimization by automating management processes supply chain.
Some examples to note are:
• Inventory reduction as a result of better visibility of stock. It allows to perform the traceability and visibility throughout the chain of production and delivery, with greater reliability and agility with current systems, which helps companies to adopt planning policies stocks more tailored to the real needs.
• Improved service level. With greater control over the delivery of orders to customers, can ensure traceability of orders much more reliable, resulting in a decrease of errors and thus returns, resulting in savings in administrative costs and increase sales.
• Improved efficiency and reduced operating costs and labor. Not being required to match in the same line of sight the reader unit and the chip, as it does with the barcode, you can resort to using bows of similar fixed reading to those found in stores to prevent shoplifting. Thus, logistics processes in warehouse management is greatly simplified the scanning operations not be necessary to identify the products in each of the phases through which pass (production, finished product warehouse, distribution center, picking, expedition, reception at the point of sale, etc.)
• Accuracy in identifying goods. As the collection of information is not dependent on manual operations, resulting in a much increased safety and accuracy in the process of ups and downs of inventories.
• Decreased shrink by shoplifting, the internal administrative errors, as a result of the aforementioned improvements.
• Better use of reusable assets Company (reusable packaging, pallets, cargo trucks, etc.)
• Fight against counterfeit products. The unique identification of products and the accessibility of such data via the Internet makes it much easier to control product marketed.
• Makes it easier and safer product recalls concrete market in the event that the existence of a threat to the safety and health of consumers discover.
Overall, identification through radiofrequency (RFID) provides significant improvement in mechanisms to track shipments across global supply chains, thus allowing both suppliers and distributors and customers, they can have real information on the number of products and delivery dates.
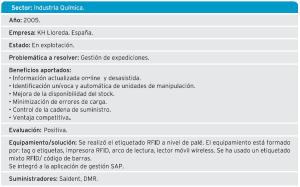
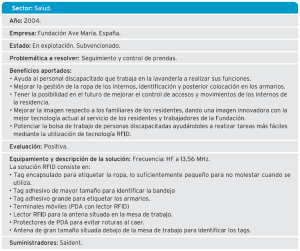
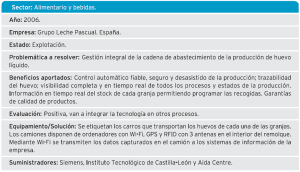
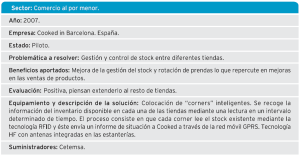
Also detect the phases of the process in which a high shrinkage rate occurs, slowdowns, etc., con el objetivo de aliviar cuellos de botella y reducir de forma considerable la falta de productos en las tiendas. Algunos Success stories:
The NFC Technology
As a particular application of RFID include the expected evolution over the next few years to NFC technology (Near Field Communications), especially the fact that it will massively built into mobile phones and therefore billions of devices on the market can be achieved.
And only bring NFC devices unos inches, automatically establishes a secure connection to transmit information (a Web address, un ticket de transporte, acceptance of payment,…), this greatly simplifies user intervention. The first applications of NFC technology are focused on mobile phones. They try to convert the only device needed to access all the services so as to allow payments, read information signs (Poster inteligente10), store the entries transportation tickets, transfer files, etc..
Internet of Things
New concepts that have recently emerged more strongly as a vision for the future use of the Internet and are closely linked to the development of RFID technology, is the concept of "Internet of Things".
Internet has transformed the daily lives of many people by allowing connection to each other without barriers of time or distance. But in the next 15 years will be a new revolution based on the extension of the concept of connecting computers and people connection objects: There will be an impressive number of interconnected objects online, even more than the growing number of people who surf the web. The fridge will exchange information with the supermarket shelves, communicate the washer with the clothes and the clothes we wear can "talk" to the objects with which we are. This connection and the physical universe's virtual Internet is the 'Internet of Things'. This view adds the terms "Internet" and "thing" or something, and means not only allow connectivity to fixed sources of information but any identifiable and achievable physical element that may have information of interest and may serve to third party access, evidently the development of this concept will affect all aspects of daily life and business.
In this sense the use of RFID technology in everyday objects become "smart objects" so that for example, elderly or disabled people may be helped by smart devices; monitoring and continuous monitoring of products in the supply chain will increase food security; "intelligent" industrial products may store information about its components and their use; waste management may target from the current overcrowded vision products for each specific type of waste performances improving the efficiency of recycling systems, Examples of fields of action in which the operation of the Internet of Things will enable breakthroughs.
Necessary to support this Internet of Things infrastructure is developing rapidly. The mobile Internet services and the deployment of next-generation mobile networks with higher speed data transport allowing the user connection from virtually anywhere and therefore access to networks anytime, actually making the concept of permanent connectivity. The extension of Internet objects is expected as one of the main applications of technologies such as radio frequency identification (RFID), detection technologies and nanotechnology. The combination of these technologies creates the increasingly frequent "smart" objects.
Detection technologies, such as wireless sensor networks, are the bridge between the physical and virtual worlds, the medium that allows objects to respond to changes in the environment. Detecting wireless networks are common in many applications:
Protected Access, environmental monitoring and home automation.
A significant drop in prices making it possible to generalize these systems detectors.
The impact of these technologies, either each of them or combined use, be extraordinary and will open a field of opportunities and entirely new business models.
If you liked this article click one i like and share.






Ferran,
Excelente artículo sobre RFID y NFC
Un saludo,
Mario
Muchas gracias Mario.
Un saludo,
Ferran R.
I got what you intend, thankyou for putting up.Woh I am lucky to find this website through google. Being intelligent is not a felony, but most societies evaluate it as at least a misdemeanor. by Lazarus Long. ebdfdddeedecbdge
Es la primera vez que escribo en tu blog aunque ya llevo unos días leyéndolo, muy buen artículo, ya estas entre mis visitas diárias. Regards.
Muchas gracias Rosena. Regards,